Semaglutide Weight Loss Results
Understanding Obesity and Weight Loss Challenges
Obesity is a major public health issue with an increasing prevalence worldwide. Excess body fat is associated with various comorbidities, as well as increased overall mortality risk.

Why Weight Loss Requires More Than Lifestyle Changes
The benefits of weight loss are evident by the reductions in morbidity and mortality. The foundation for most weight loss programs involves strict lifestyle modification, including dietary change and exercise.
Unfortunately, many individuals struggle with weight loss and chronic weight management due to difficulty adhering to long-term lifestyle modification and the metabolic adaptations that promote weight regain. The use of adjunctive pharmacotherapy has been employed to help patients not only achieve greater weight loss than lifestyle modification alone, but also to assist with long-term weight management.
Historically, anti-obesity drugs have produced only modest weight loss and required at least once daily administration. Semaglutide or Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), a hormone with significant effects on glycemic control, appetite, and weight regulation, is a new therapy being used for weight loss.
What is Semaglutide?
Semaglutide, a GLP-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1RA), was recently approved by the Food and Drug Administration for chronic weight management in adults with obesity or who are overweight. The approval came after the publication of the Semaglutide Treatment Effect in People with Obesity (STEP) clinical trials. In these 68-week trials, semaglutide was associated with significantly greater weight loss compared to placebo. Semaglutide differs from other GLP-1RAs by having a longer half-life and producing greater weight loss.
Why Long-Term Weight Management Requires Medical Support

As a chronic and relapsing disease, obesity impairs metabolism and causes cardiovascular disease. Although behavioral modification is important for the treatment of obesity, it is difficult to achieve an ideal weight or sustain the process of long-term weight loss.
Therefore, the obesity control guidelines strongly recommend lifestyle interventions along with medical treatment for patients who are overweight and in need of clinically significant weight loss to reduce cardiometabolic risk factors. There is sufficient evidence supporting that pharmacotherapy in combination with behavior-based interventions can result in significant weight loss and improved cardiometabolism, lessening cardiovascular risk factors.
Semaglutide and Diabetes Management
Semaglutide is used along with a diet and exercise program to control blood sugar levels in adults with type 2 diabetes (condition in which the body does not use insulin normally and therefore cannot control the amount of sugar in the blood) when other medications did not control the sugar levels well enough.
Semaglutide is not used to treat type 1 diabetes (condition in which the body does not produce insulin and therefore cannot control the amount of sugar in the blood) or diabetic ketoacidosis (a serious condition that may develop if high blood sugar is not treated).
Semaglutide is in a class of medications called incretin mimetics. It works by helping the pancreas to release the right amount of insulin when blood sugar levels are high. Insulin helps move sugar from the blood into other body tissues where it is used for energy. Semaglutide also works by slowing the movement of food through the stomach.
How BMI Is Used to Assess Weight Status
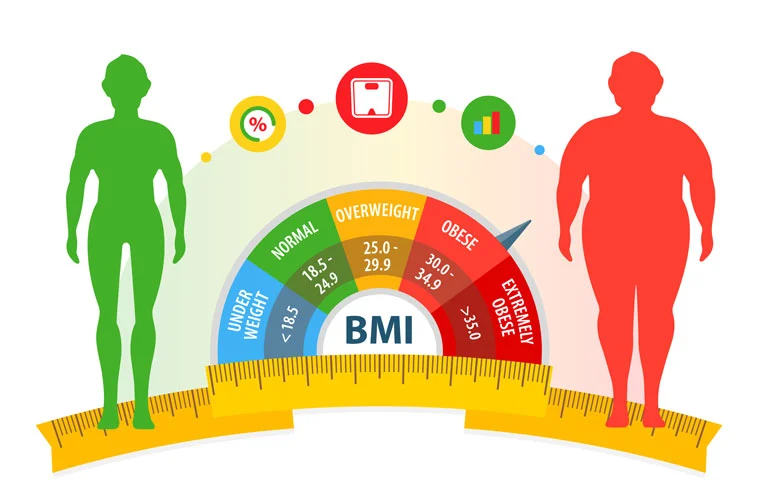
You can find an estimated body fat percentage by utilizing your height, baseline body weight, and a current BMI (Body Mass Index) chart. Once you know your body fat percentage, you can more easily calculate your lean body mass relative to that percentage.
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a person’s weight in kilograms (or pounds) divided by the square of height in meters (or feet). A high BMI can indicate high body fatness. BMI screens for weight categories that may lead to health problems, but it does not diagnose the body fatness or health of an individual.
Understanding Your BMI Results
A high or low BMI may be an indicator of poor diet, varying activity levels, or high stress. Just because someone has a ‘normal BMI’ does not mean that they are healthy.
BMI doesn’t take account of body composition, for example, muscle, fat, bone density. Sex and other factors which can impact your weight can also lead to an inaccurate reading. As such a BMI calculation is not a suitable measure for some people including children and young people under 18, pregnant women and athletes.
BMI Ranges Explained
Your BMI will fit into one of 5 bands:
- under 18.5 – This is described as underweight.
- between 18.5 and 24.9 – This is described as the ‘healthy range’.
- between 25 and 29.9 – This is described as overweight
- between 30 and 39.9 – This is described as obesity
- 40 or over – This is described as severe obesity
Reaching Your Ideal Body Weight With Semaglutide
For those who have suffered with weight gain and weight maintenance, possibilities as extreme as bariatric surgery may have been considered. Semaglutide, administered at a dose of 2.4 mg, helped most people with obesity in a clinical trial lose at least 10 percent of their body weight, and more than half of them reduced their weight by at least 15 percent, according to the study results, which were published in February 2021 in the New England Journal of Medicine.
People taking semaglutide also experienced greater improvements in cardiovascular risk factors like BMI, waist circumference, blood pressure, and blood sugar than participants given a placebo.
Semaglutide Weight Loss With Tucson Wellness MD
At Tucson Wellness we are dedicated to helping you be better in everything you do. Excess weight can hurt your overall health and cause disease and injury that might otherwise be prevented. We use safe, natural, and effective methods to help with weight loss and keep it off.
Learn if you might be a good candidate with a consultation with our Master Medical Nutritionist. Learn more and contact us today by continuing to explore our website.